After radioactive cesium is ingested it is distributed fairly uniformly throughout the bodys soft tissues. Risk assessment ra.

Ionizing Radiation Wikipedia
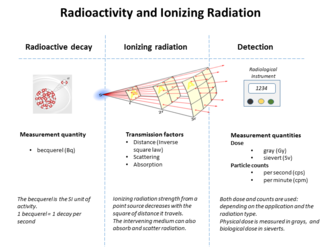
The measurement of emissions from radioactive material in the body is. For example the amount of radiation being given off or emitted by a radioactive material is measured using the conventional unit curie ci named for the famed scientist marie curie or the si unit becquerel bq. Slightly lower concentrations are found in bone and fat. Occur when the body is exposed to radioactive material outside the body. 5 non imaging nuclear medicine probe 5 introduction of radioactive materials into the body for the study of distribution and fate of certain substances by the detection of. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation. By measuring the radiation level around a persons body using a geiger counter a safety officer can approximate that persons absorbed dose.
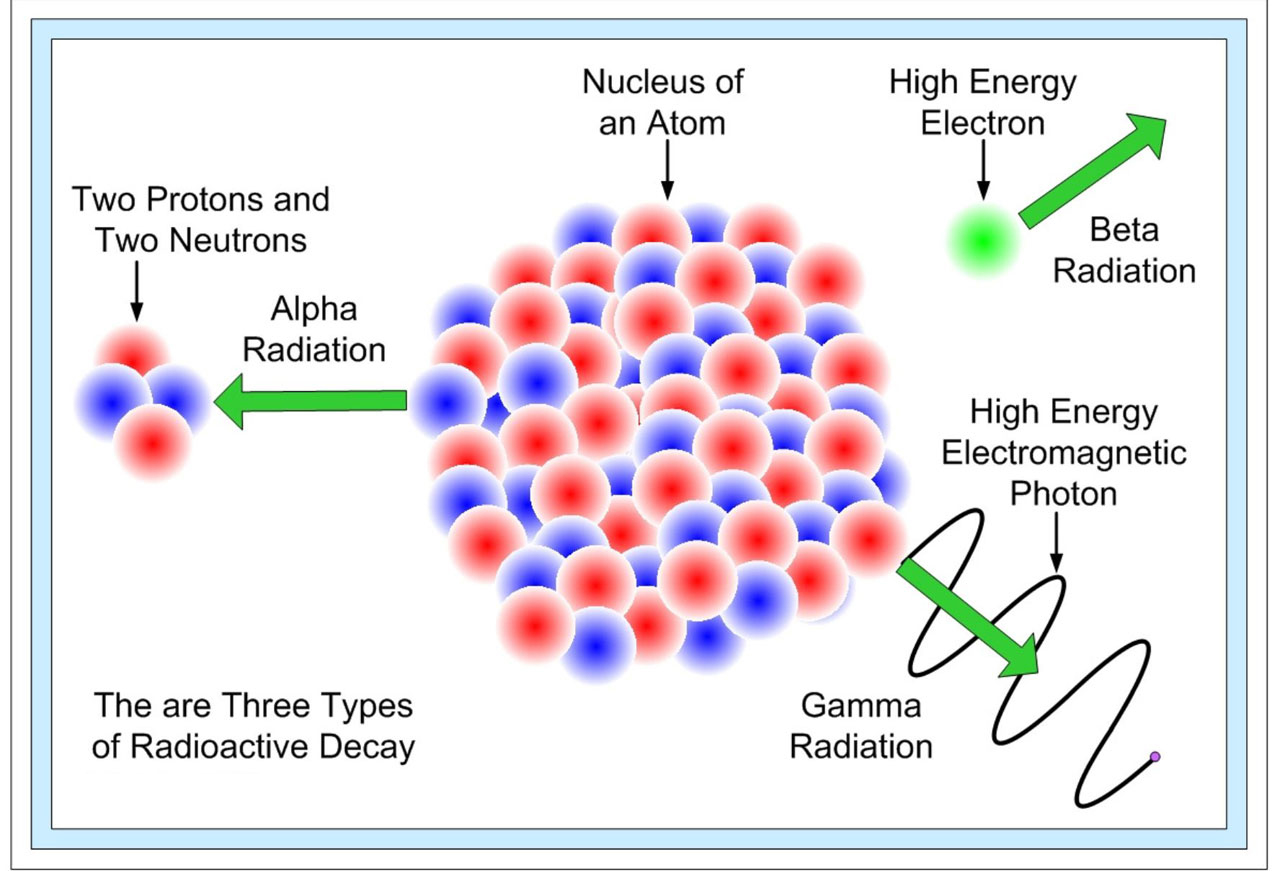
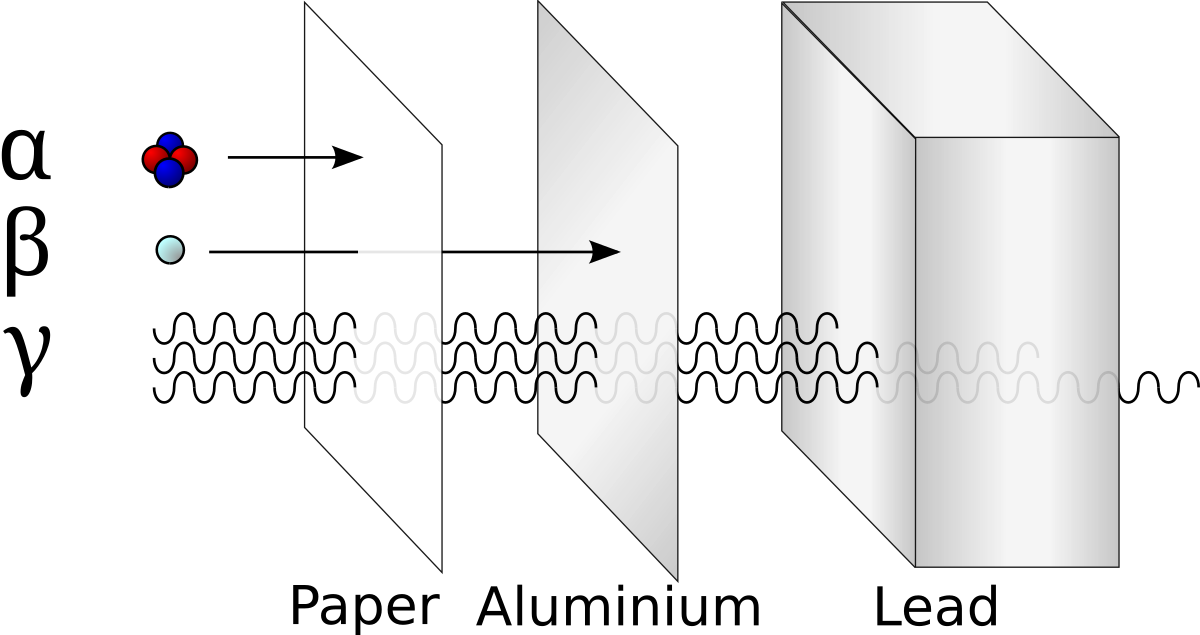
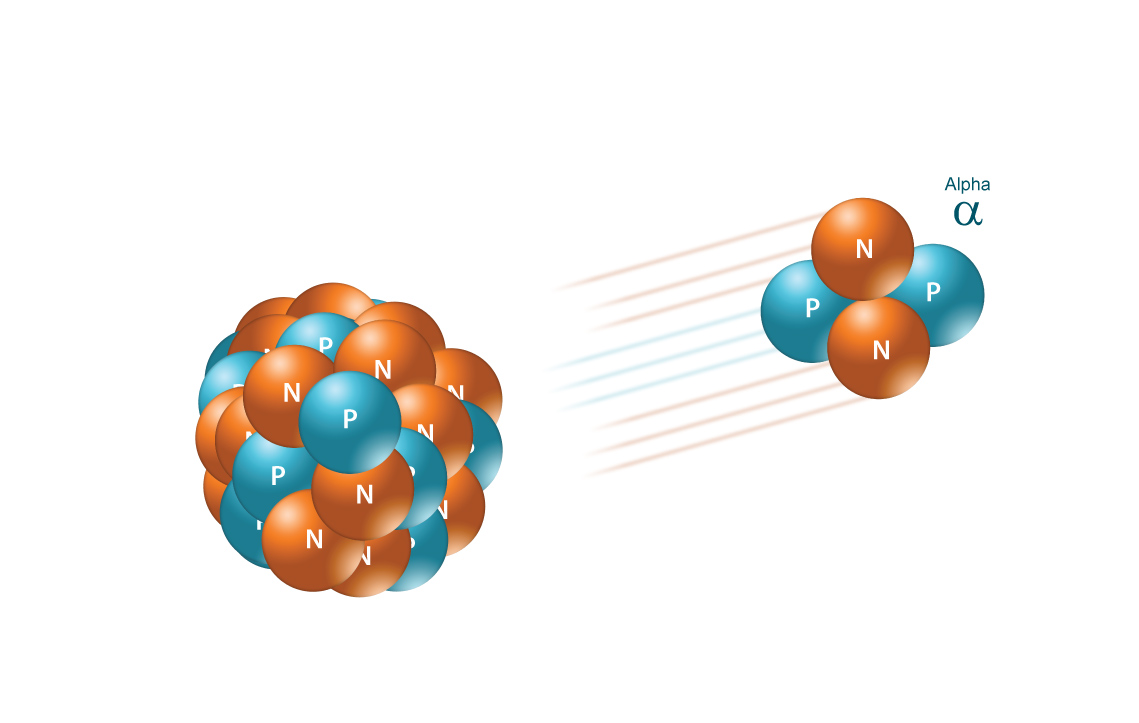
Outside the body alpha particles wont even go through the outer layer of skin. In nuclear accidents a measure of the type and amount of radioactivity released such as from a reactor containment failure is known as the source term. Effective dose is a measure of the biological damage to the whole body resulting from exposure. As used in this part. Slightly higher concentrations are found in muscle. Examples of radioactive materials that give off alpha particles are polonium 210 radon 222 radium 226 and americium 241.
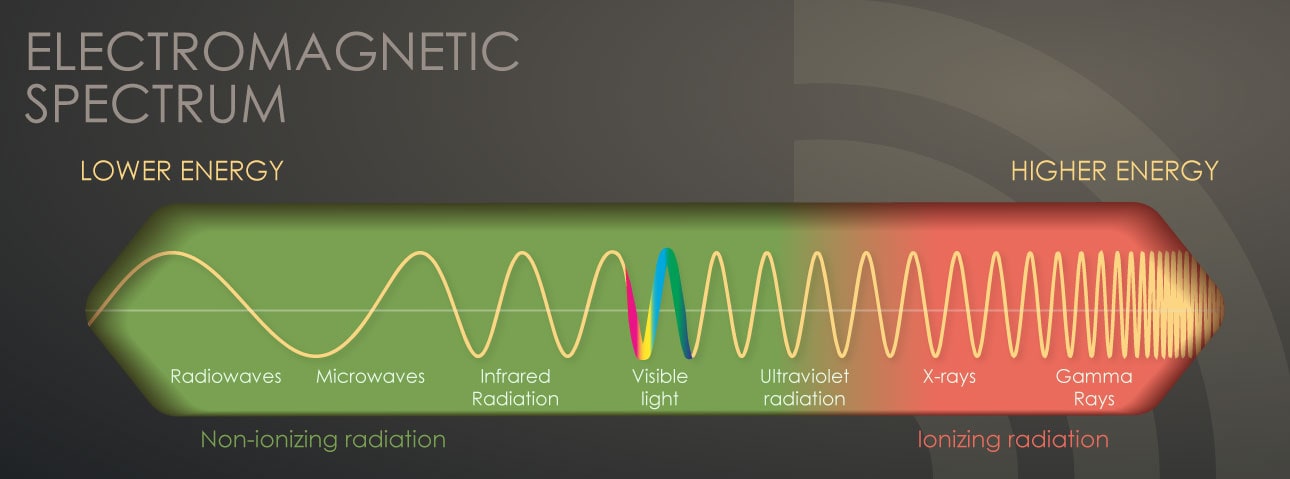
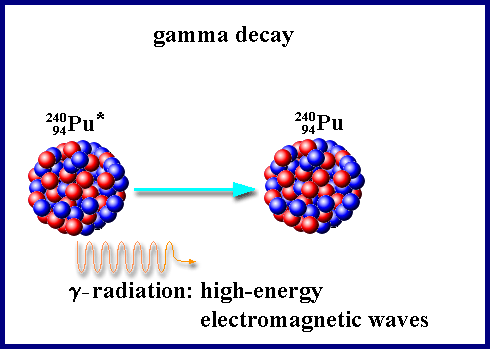
2011 et seq as amended. A more sophisticated measure of radiation exposure. The units of absorbed dose are the rad and the gray gy. Inside the body they can kill nearby cells. A radioactive element may emit gamma rays in discrete bundles or quanta called photons if the nucleus remaining after alpha or beta decay is in an excited state. Different units of measure are used depending on what aspect of radiation is being measured.
4 non imaging nuclear medicine uptake 4 introduction of radioactive materials into the body for measurements of organ functions from detection of radioactive emissions. Beta particles are electrons emitted from an atom. Cesium 137 remains in the body for a relatively short time. Accelerator produced radioactive material means any material made radioactive by a particle accelerator. Act means the atomic energy act of 1954 42 usc. Absorbed dose means the energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material.
Most gamma emissions are accompanied by beta emissions. The united states nuclear regulatory commission defines this as types and amounts of radioactive or hazardous material released to the environment following an accident. A medium energy beta particle travels about one meter in air and one millimeter in body tissue. Measurement of absorption of radioactive emissions from an external source nonimaging assay introduction of radioactive materials into the body for the study of body fluids and blood elements by the detection of radioactive emissions. Cesium 137 can enter the body when it is inhaled or ingested.