Measurement accuracy primarily depends on whether the thermometer is used correctly read the operating instructions. To none of these dilemmas exists a straight answer.
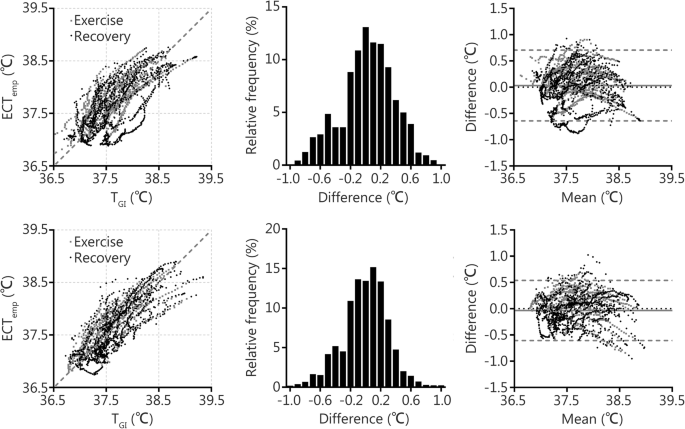
Validity Of A Noninvasive Estimation Of Deep Body Temperature
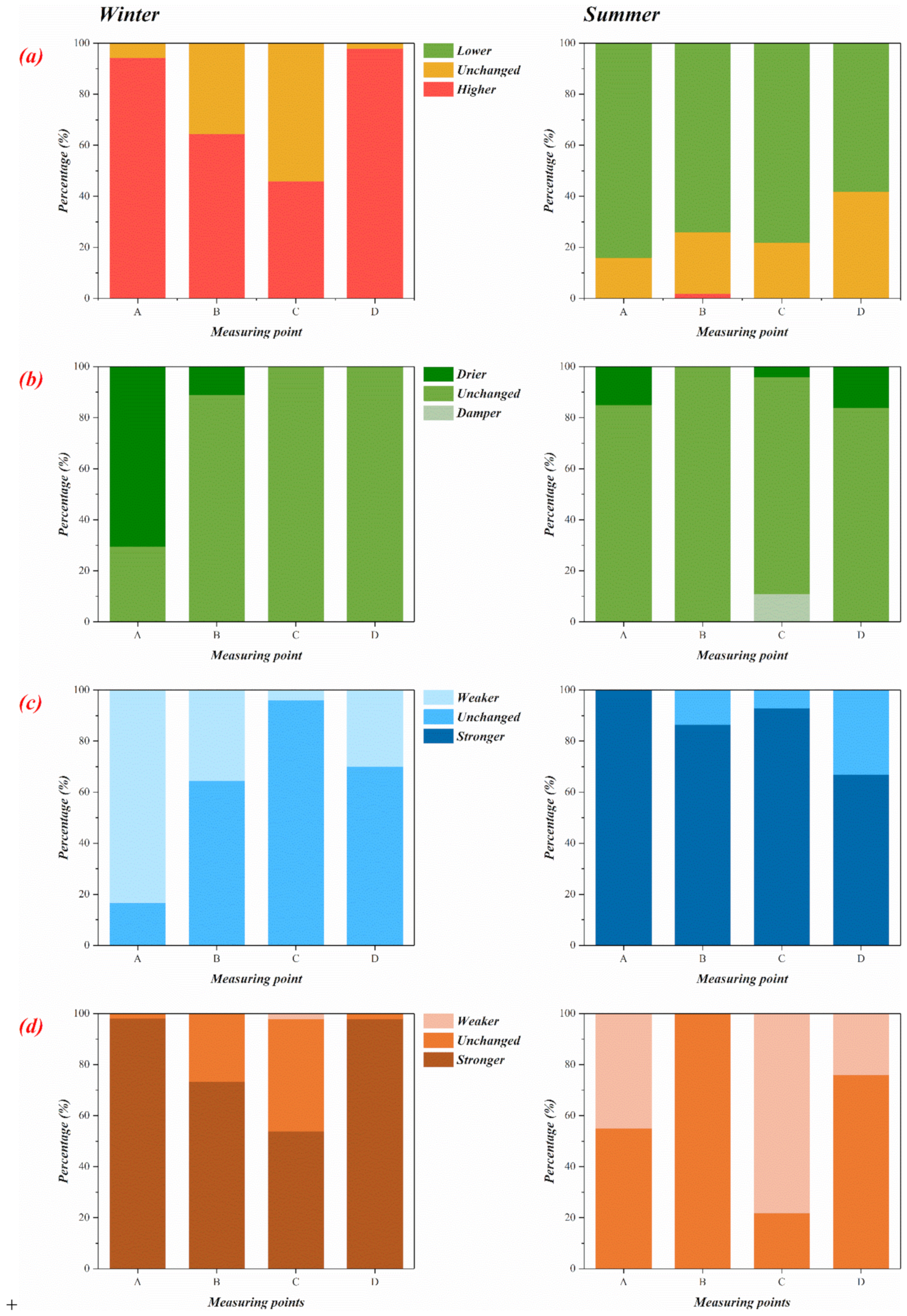
Dilemmas in measurement of human body temperature. While typically 986f 370c is considered a normal temperature some studies have shown that normal body temperature can be within a wide range from 97f 361c to 99f 372c. Presented are also calibration. Dilemmas in measurement of human body temperature. The range for normal human body temperatures taken orally is 368 05 c 982 09 f. Consequently each type of measurement has a range of normal temperatures. The measurement of core body temperature may seem simple but several issues affect the accuracy of the reading.
Body temperature is routinely measured as 1 of the 4 vital signs and when elevated triggers a search for an explanation. Pušnik i miklavec a. These include the measurement site the reliability of the instrument and user technique pusnik and miklavec 2009. Forehead skin temperature measurements using liquid crystal plastic discs were unreliable. Instrumentation science and technology 2009. However electronic thermometers should be subjected to routine checks.
Pulmonary artery and rectal temperature measurements were satisfactory in operating theatre and intensive care unit. Nonetheless scientific data that define normal temperatures in. The article describes dilemmas in measurement of human body temperature and thermometers used for its measurement. The third dilemma is how to measure human body temperature namely which thermometers to use. Presented are also calibration results of certain clinical radiation thermometers and their improvement in the past few years in terms of accuracy and uncertainty. Normal human body temperature varies slightly from person to person and by the time of day.
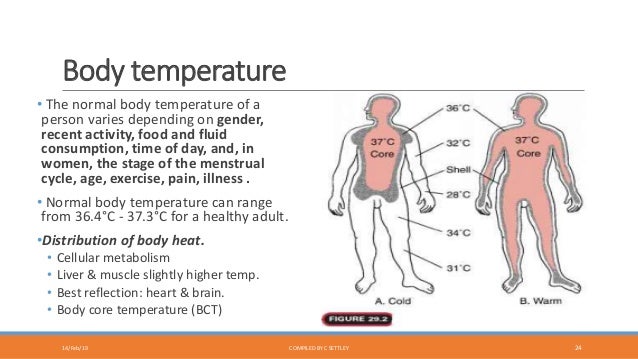
Contrary to the widespread view there is no normal temperature. The first dilemma in measurement of human body temperature is what could be considered as normal or as increased body temperature. The article describes dilemmas in measurement of human body temperature and thermometers used for its measurement. The second dilemma is where to measure human body temperature in terms of body sites. The body temperature measured is always dependent on where the measurement is taken. This is due to physiological factors and must be distinguished from thermometer malfunction.
To none of these dilemmas exists a straight answer.